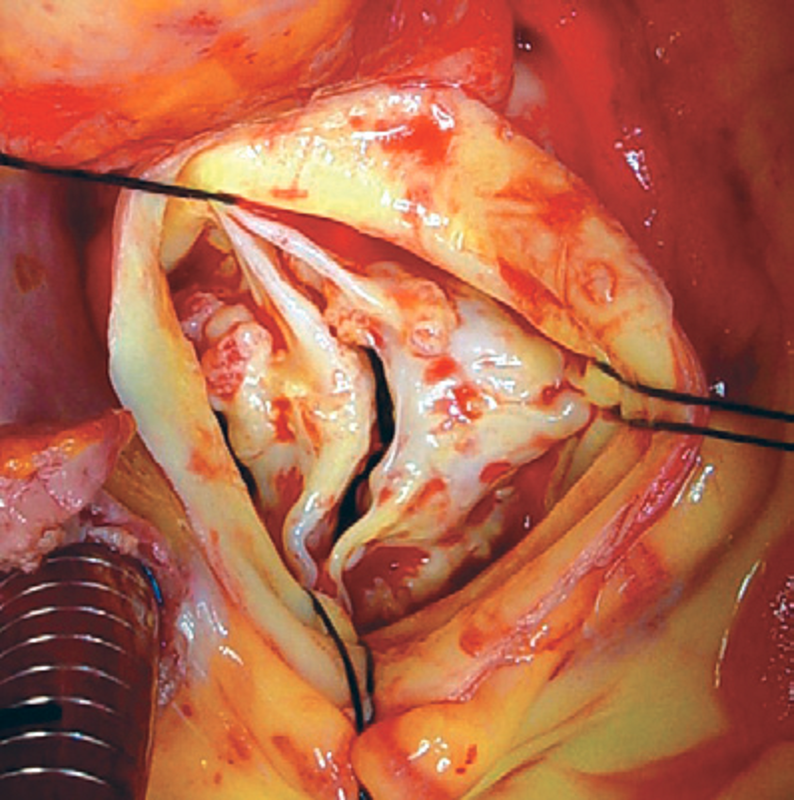
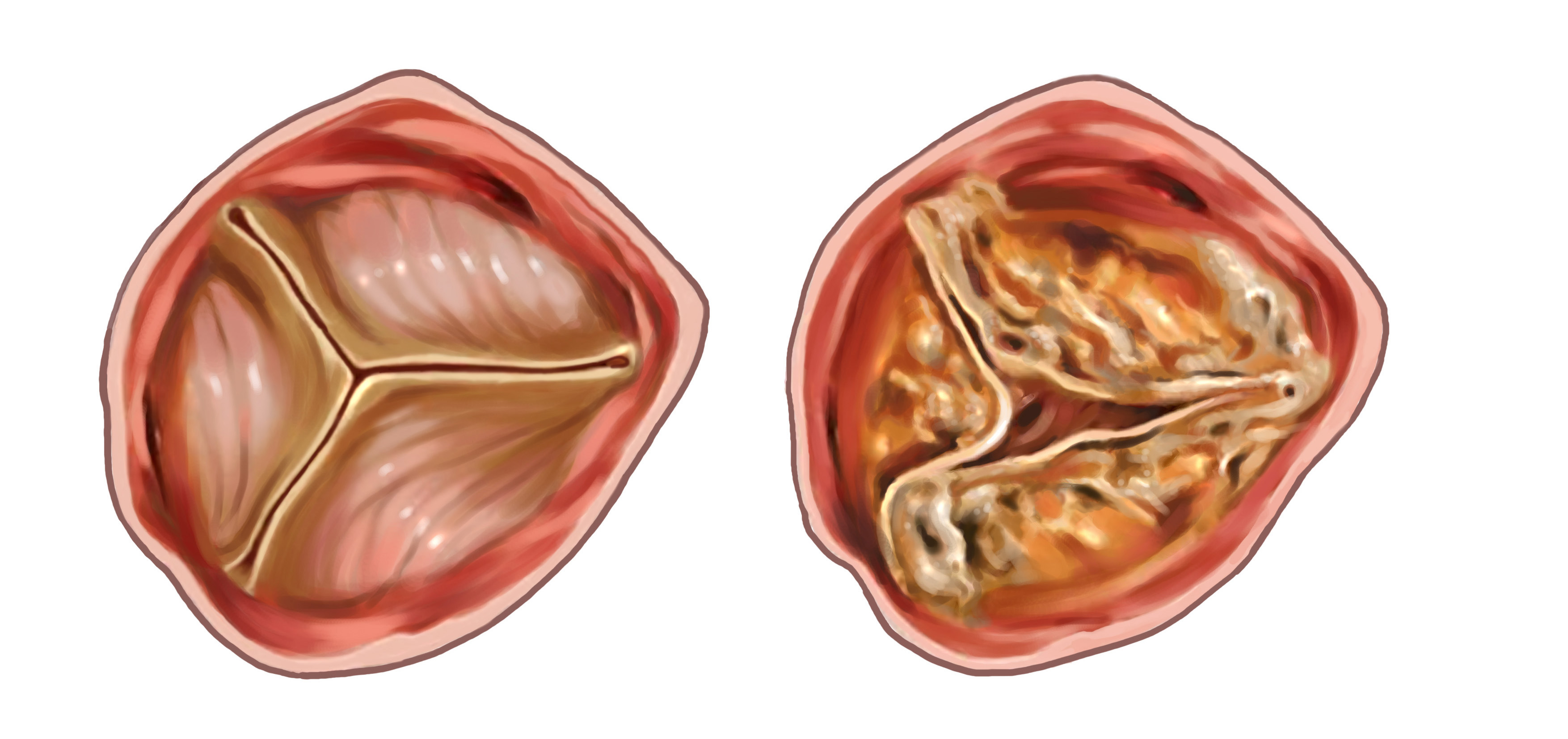
Aortic stenosis may be caused by rheumatic disease, a congenital bicuspid valve or calcification of a trileaflet valve. Your aortic valve does not open fully, so blood flow out of the heart is reduced.
The aorta is the big artery supplying your body with oxygen rich blood.
Aortic valve stenosis surgery. The aortic valve can be surgically replaced in three ways: The aortic valve controls the flow of blood out from the heart to. 1,2 in the cardiovascular health study, which involved 5201 men and women >65 years of age, the.
If you have been diagnosed with severe aortic stenosis, you may have to decide whether to fix your valve. So you know, normal aortic valves have three tissue leaflets (or. The operative mortality for aortic valve replacement has improved dramatically over the past 4 decades and remains the only effective therapy for severe symptomatic aortic stenosis.
Surgery for asymptomatic aortic valve stenosis * surgery is not traditionally considered for the asymptomatic patient, regardless the degree of stenosis, because the risk of sudden death is considered to be low (estimated at<1%/year), and the risk of the avr may exceed the potential benefit of surgery.; Then the pulmonary valve is replaced with a preserved donor pulmonary valve. Etiologies include congenital (bicuspid/unicuspid), calcific, and rheumatic disease.
Valve movement after deployment, blockage or disruption of blood flow through the heart, need for additional heart surgery or emergency heart surgery and possible removal of the edwards sapien 3 ultra and sapien 3 valves, a blood clot that requires treatment, damage to the valve (e.g., wear, breakage, recurring aortic stenosis), valve issues. The study, the aortic valve replacement versus conservative treatment in asymptomatic severe aortic stenosis (avatar) trial, was designed to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of performing aortic valve replacement surgery earlier for adults who are asymptomatic and have normal left ventricle function. The purpose of this study was to determine median survival time in relation to.
Many young people with aortic stenosis will need aortic valve replacement surgery at some point in their lives. The authors hypothesize that increased cardiac risk during noncardiac surgery is associated with an aortic valve area ≤0.7 cm 2 and mean gradient ≥50 mm hg. Aortic valve surgery is performed by heart surgeons to treat most commonly bicuspid valves, other congenital aortic valve diseases, aortic valve stenosis, and aortic valve regurgitation.
5, 6 ace is also found in atherosclerotic lesions and angiotensin ii is assumed to contribute to the. The aortic valve can be replaced using: Stenosis, when the opening of the valve gets too narrow and not enough blood flows out.
Those problems can cause shortness of breath,. Tavr is also referred to as transcatheter aortic valve implantation, or tavi. Surgical risk, age, perceived life expectancy, and valve durability influence the choice between surgical aortic valve replacement (savr) and transcatheter aortic valve implantation.
For people experiencing severe aortic stenosis who do not have symptoms or need symptom relief, early aortic valve replacement surgery may be beneficial because it reduces the risk of death, heart. Open aortic valve surgery, done by making a. The contemporaneous life expectancy after savr, in relation to surgical risk and age, is unknown.
There are many different causes of of this disease including congenital birth defects, infections, and degenerative conditions (like aging). Minimally invasive aortic valve surgery, done using one or more small cuts. When a valve becomes narrow, or stenotic, it can negatively impact the flow of blood through the heart and the body.
Ad severe aortic stenosis (sas) who is experiencing symptoms and needing valve replacement? Your aortic valve does not open fully, so blood flow out of the heart is reduced. Aortic stenosis may be caused by rheumatic disease, a congenital bicuspid valve or calcification of a trileaflet valve.
This valve opens to let blood flow from your heart to your aorta. Some of you will have. In adults with valvular stenosis, the importance of prompt aortic valve replacement once symptoms occur is well known.
Mild aortic stenosis will require an echocardiogram from 3 to 5 years. Aortic stenosis is a tightening of the aortic valve in the heart. The aorta is the big artery supplying your body with oxygen rich blood.
The acc/aha and esc/eacts guidelines have lowered the threshold for surgery in asymptomatic patients with as • severity of as • severity of calcification • left ventricular function • exercise response (1) the ross procedure, a surgery in which the abnormal aortic valve is removed and replaced by the child’s own pulmonary valve. Very severe aortic stenosis with peak velocity >5.5 m/s;
This is called aortic stenosis. In europe and north america, the aetiology of aortic stenosis most often is increased leaflet stiffness,. (2) aortic valve replacement with a preserved donor valve.
Ad severe aortic stenosis (sas) who is experiencing symptoms and needing valve replacement? If it is moderate, expect to have an echocardiogram either annually or biennially to monitor how the condition is progressing. An aortic valve replacement is a type of open heart surgery used to treat problems with the heart�s aortic valve.
Life expectancy surgery</strong> group, 92.3% underwent surgical avr This information will help you understand the conditions that may affect the aortic valve and why surgical treatment may be needed to treat your condition. Severe as need to be followed carefully for the development of symptoms.
Aortic stenosis is a common valvular disorder leading to left ventricular outflow obstruction.[1] the anterograde velocity across the valve must be at least 2 m/sec, whereas the aortic valve sclerosis is the thickening and calcification without a significant pressure gradient. Aortic stenosis and chronic aortic regurgitation. The timing of aortic valve surgery is described for patients presenting with two conditions:
Aortic stenosis (as) means that your aortic valve cannot open fully. Previous coronary artery bypass grafting or heart valve surgery; The cardiac risk during noncardiac surgery in patients with as appears to have decreased compared to historical reports, perhaps due to an increased awareness of hemodynamic concerns.
Treatments may include transcatheter aortic valve replacement (tavr), surgery or symptom management. Future echocardiograms may be scheduled according to the severity of your condition.