
The beach chair provides anterior and lateral access to the shoulder joint while prohibiting posterior open approaches. Surgical beach chair (fowler�s position) designed for orthopedic shoulder procedures;
• surgeries requiring beach chair positioning increasing in frequency • devastating neurological sequelae in healthy patients have been reported • lower limit of autoregulation?
Beach chair position surgery. [] describe patient, surgical, and institutional factors associated with the perioperative installation of arterial lines for blood pressure monitoring during tsa to allow anaesthesiologists to “benchmark” with. During procedures in the bcp or sitting position, the head should be secured in a neutral position to avoid flexion or extension. The senior author (m.t.f.) prefers labral work in the lateral decubitus position and all other procedures in the beach chair position.
Surgical beach chair (fowler�s position) designed for orthopedic shoulder procedures; Surgery to the shoulder may be performed with patients seated upright in a position known as the beach chair position (bcp). this position has certain advantages compared to alternative surgical positions (e.g. • surgeries requiring beach chair positioning increasing in frequency • devastating neurological sequelae in healthy patients have been reported • lower limit of autoregulation?
The advantages of the beach chair position include the ease of setup, limited brachial plexus stress, increased glenohumeral and subacromial visualization, anesthesia flexibility, and the ability to easily convert to an open procedure. As a general rule, a minimum of. This is often used in shoulder procedures to facilitate surgical access and minimize bleeding.
Induction of anesthesia the choice of shoulder arthroscopy position is surgeon dependent. Universal connection to nearly all general surgical tables; Focus on the positioning technique for the beach chair position.
The beach chair position for shoulder surgery in intravenous general anesthesia and controlled hypotension: The beach chair position is a reliable, safe, and effective position to perform nearly all types of shoulder arthroscopic procedures. Arthroscopic shoulder surgery can be performed in both the beach chair and lateral decubitus positions.
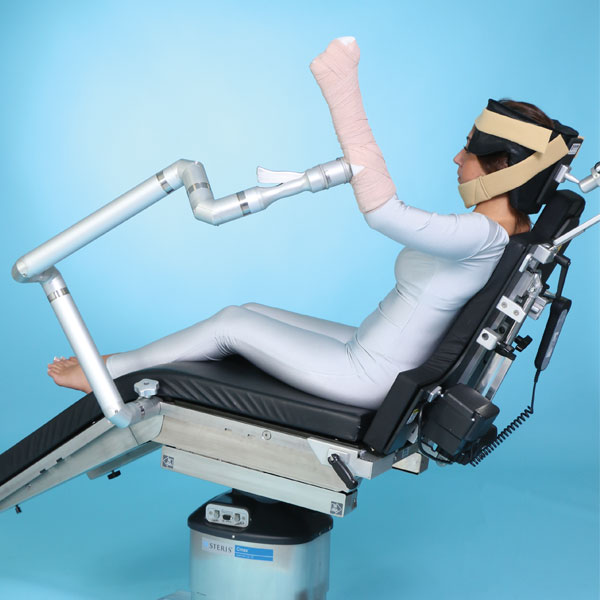
Surgical patient weight capacity ; A beach chair position is utilized though the head of the bed is elevated approximately 60 [degrees] to 70 [degrees], a position slightly more vertical than normal. Designed to attach to the rails of almost any or table superior head adjustment allows for infinite positions of tilt, rotation, and forward slide of the head
It is helpful to place the trunk almost upright with an almost hanging arm to help reduce the fracture by ligamentotaxis and gravity. Hypotension can occur due to venous pooling in the lower limbs and the vasodilatory effects of general anaesthesia. 1,2 this position affords better intraarticular visualization and less risk of neurovascular trauma than when patients are placed.
No guidelines currently exist for invasive perioperative blood pressure monitoring in patients undergoing tsa in the beach chair position. The mechanism of neurologic injury in the beach chair position is unknown but , In this issue, gabriel et al.
Tance and there is much debate about the optimum position for surgery. The beach chair provides anterior and lateral access to the shoulder joint while prohibiting posterior open approaches. • allow for hydrostatic gradient and keep the blood pressure up • no widely agreed monitoring standard • increasing fio 2 and etco 2
Setting up the patient to the beach chair position for shoulder surgery on merivaara promerix operating table. Open shoulder surgery or arthroscopy performed in the sitting position under interscalene block may be complicated by episodes of bradycardia or hypotension, or both, which occurs in up to 20% of cases. The beach chair position allows better surgical visualization compared to lateral decubitus position but may be associated with catastrophic neurologic complications, including stroke, spinal cord ischemia, and transient visual loss.
The beach chair position is a reliable, safe, and effective position to perform nearly all types of shoulder arthroscopic procedures. This can result in brain damage, but an understanding of cerebral autoregulation is. Typically the patient is placed in 10⁰.
The present report describes optimal management of cerebral oxygenation during arthroscopic shoulder surgery performed in the beach chair position. The beach chair position [bcp] is extensively used as a routine approach for shoulder surgery in australia, new zealand and around the world. Shoulder surgery in the beach chair position is associated with diminished cerebral autoregulation but no differences in postoperative cognition or brain injury biomarker levels compared with supine positioning:
However, it has been found that surgery in the bcp can temporarily decrease the amount of oxygen in. One of the surgical procedures most commonly performed in north america is arthroscopic repair of the shoulder joint. Antegrade nailing, anterolateral/anterior plating and external fixation may all be performed in the beach chair position.
The beach chair position allows better surgical visualization compared to lateral decubitus position but may be associated with catastrophic neurologic complications, including stroke, spinal cord ischemia, and transient visual loss. Shoulder procedures in the beach chair position.¹ it places the surgeon, anesthesiologist and surgical staff in an optimal position to position patients. Relationship between the beach chair position and cerebral hypoperfusion3,4, and it is widely accepted that the beach chair position may be associated with a decrease in cerebral perfusion5,6.
In 2005, pohl and cullen (19) reported four cases of ischemic brain and spinal cord injury after shoulder surgery in the beach chair position. The anesthesia patient safety foundation beach chair study. Side effects of the beach chair position.
Side lying) in some situations. Impact on cerebral oxygenation, cerebral blood flow and neurobehavioral outcome In patients who are anesthetized for surgery in the beach chair position, brain blood pressure can fall to levels below the brain’s ability to autoregulate.
Proper patient positioning is crucial as incorrect positioning will keep the surgeon from performing a successful operation.