In addition, some risks of si joint surgery include incomplete pain relief, damage to the nerve roots, infection, and complications with the hardware. It is where the sacrum meets the.

All three ultimately had resolution of radicular pain.
Si joint fusion surgery complications. The sacroiliac joint, also known as the “si joint,” is located at the bottom of the spine. Si joint problems are a common cause of low back pain which can also include debilitating symptoms including pain in the thigh and/or buttock, and possibly pain that radiates down the sciatic nerve. Los angeles sacroiliac joint fusion (si joint fusion) surgery denial lawyer.
Allergic reaction to or rejection of the implants; Complications during the operation can make the condition worse and take more time, eventually. Si joint pain decreased from 76.2 at baseline to 35.1 (54% reduction, p <.0001).
Increased pain in the sacroiliac joint or surrounding tissues and joints; What does recovery from sacroiliac joint fusion look like? Dysfunction in the sacroiliac joint (also called the si joint) can produce significant lower back pain, as well as pelvic, groin, and hip pain.
The overall complication rate was 13.2 at 90 days which increased to 16.4% at 6 months. As with any surgery, sacroiliac joint fusion poses risks and possible complications during or following surgery. A revision procedure (2%) for nerve impingement and 1 case of ongoing low back pain.
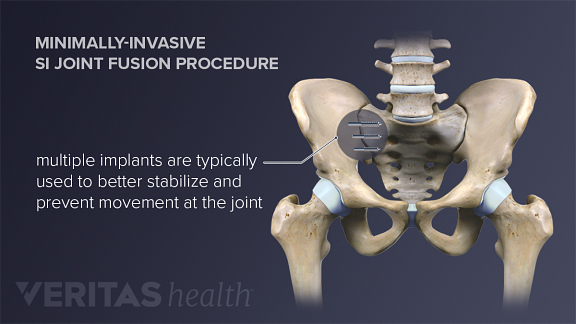
Muscle pain due to the change in function of the si joint; Nicotine and tobacco products increase the risk of postoperative complications. Minimally invasive si joint surgery is the current medical standard of care for si joint fusion to relieve sacroiliac joint pain.
Odi decreased from 55.5 to 35.3 at 6 months (p <.001). Among these patients, an overall complication rate of 13.2% (n=62) was seen at 90 days postoperatively and 16.4% (n=77) at 6 months. Sacroiliac fusion is a surgical procedure which involves fusing of the iliac bones and sacrum for stabilization.
It is where the sacrum meets the. Sacroiliac joint dysfunction can be the result of too much motion, too little motion, or inflammation of the joint. This joint connects the sacrum (tailbone) to the pelvis.
In addition, some risks of si joint surgery include incomplete pain relief, damage to the nerve roots, infection, and complications with the hardware. Stress to and fracture of the bones in the pelvis surrounding the implants; Three important complications you need to know about si joint surgery are failure to fuse, failure to relieve the pain, and adjacent segment disease.
Recovery following a si joint fusion surgery depends upon the severity of symptoms, the types. Open arthrodesis procedures reported in the literature require relatively large incisions, significant bone harvesting, and lengthy hospital stays; Failure to fuse despite screws or inserted implants, the bones may not fuse together creating instability and pain.
Minimally invasive si joint fusion provides clinically significant improvement in pain scores and disability in most patients, across multiple studies and implant manufacturers. Three complications described by screw malposition with neurologic deficit (6.7%) were treated with screw repositioning (1 case) and removal of a single superior implant (2 cases) with time to revision of 2.2 months. Most of these complications can be treated once they are detected, but sometimes they require a longer period of hospitalization or recovery, additional medications, and sometimes even additional surgery.
As with all major invasive surgical procedures, some complications are possible with si joint fusion surgery as well. All three ultimately had resolution of radicular pain. All this being said, about 10% to 15% of all si joint fusions suffer significant complications.
Neurosurgeons use fluoroscopic imaging to guide and implant instruments into the sacroiliac joint throughout the surgery. Indication your doctor may recommend sacroiliac fusion surgery if you are experiencing severe sacroiliac joint dysfunction due to arthritis, injury due to accidents or falls, being overweight, uneven leg lengths, gout, and spondylitis. Migration, loosening, breakage or failure of the implant;
Proven effectiveness [see clinical results] The number of patients receiving a first time diagnosis of lumbar pathology following minimally invasive si fusion in the sample population was also analyzed. Quit smoking before surgery smoking before surgery increases risks after surgery and slows the healing process.
The risks and complications are similar to those of spinal surgery and therefore for more detailed information about the general risks and complications please look at the ‘risks and complications’ section. 469 patients who underwent si joint fusion were followed from 2007 to 2014. During the procedure, risks include excessive blood loss or complications due to anesthesia;
These factors include infection, failure to fuse, continuing or worsened postoperative pain or other occurrence that eventually leads of some 2% to 5% of all sacroiliac surgeries being called failures. Porous titanium surface allows for bony ongrowth/ingrowth 17; Postoperative infection, nervous system, pain, urinary tract infection, osteomyelitis and joint derangement.
The corresponding records data was evaluated for novel postoperative complications in six categories; Anesthesia thrombophlebitis infection nerve damage implant/hardware Every reviewed study reported clinical benefit in terms of improved pain scores or improvement in validated disability measures.
Opioid use decreased from 66% to 30%. Titanium construction designed specifically to stabilize and fuse the si joint; Patients also reported the onset of new low back pain after si joint fusion with an incidence of 3.6% at 90 days and increased to 5.3% at 6 months.