
Conservative versus surgical management for patients with rotator cuff tears: The goal of rotator cuff repair surgery is to help restore the function and flexibility of the shoulder and to relieve the.
Often patients with rotator cuff tears come into the office complaining more of weakness, while patients with rotator cuff tendonitis (bursitis) complain predominantly of pain.
Surgery for rotator cuff tears. At the moment, we are uncertain whether rotator cuff repair surgery provides clinically meaningful benefits to people with symptomatic tears; When repeated tearing occurs, the fabric of the tendon becomes weakened and finally, like the cloth at the knees of old trousers, splits. Rotator cuff tears do not heal on their own without surgery, but many patients can improve functionally and decrease pain with nonsurgical treatment by strengthening their shoulder muscles.
Sometimes, the rotator cuff tears off of. The ongoing debate surrounding the role of surgery in the management of symptomatic atraumatic rotator cuff tears is reminiscent of the debate surrounding surgery for the management of degenerative meniscus tears in older patients—another area where reasonable randomized trials have found no benefit to surgery, yet surgeons continue to. This is both because surgery indicates your rotator cuff tear was serious, and also because surgery is invasive and requires longer recovery times and results in more medical expenses.
Repair or fixation of the torn tendons to bone is the most common surgery recommended to individuals with a rotator cuff tear that either happened because of a substantial injury or has not responded to physical therapy (arthroscopic repair of the rotator cuff: A rotator cuff tear occurs when one of the supportive tendons. Research has shown that nearly 60% of these large rotator cuff surgical repairs actually fail, resulting in retears.
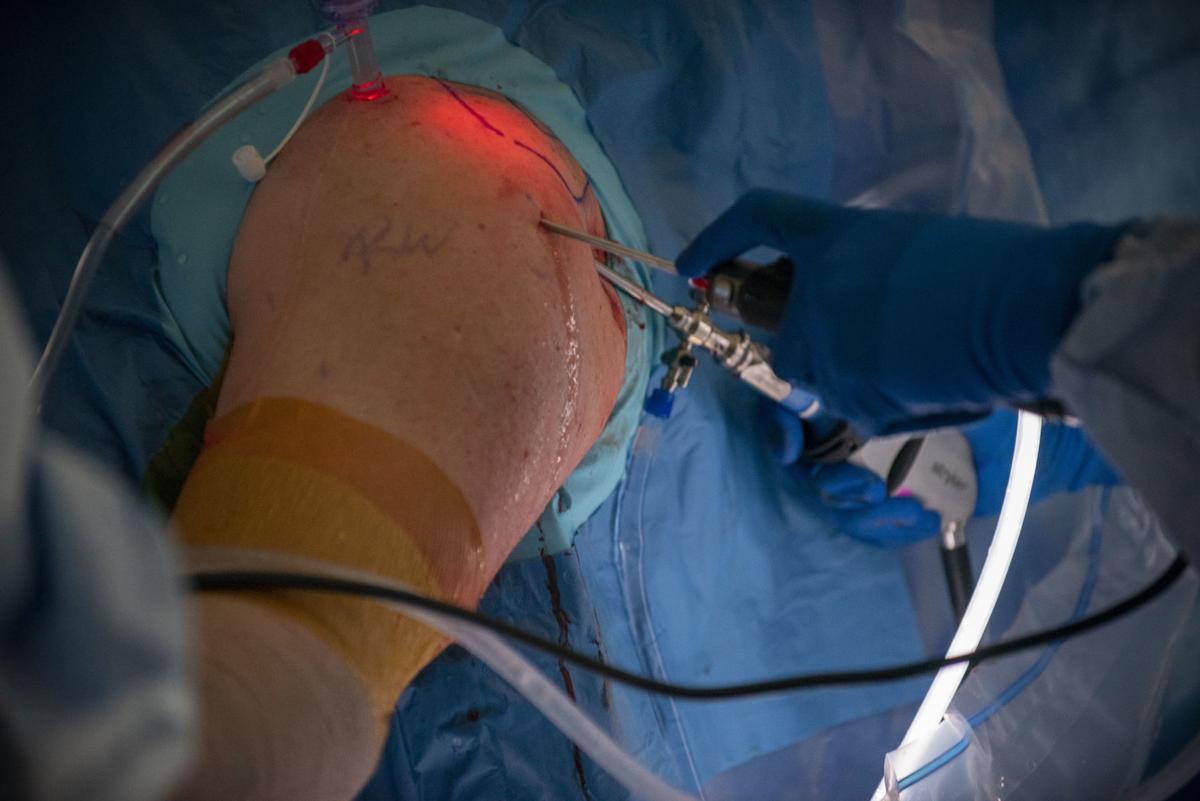
Using these small incisions can reduce pain and improve recovery long term. Along with this issue is inflammation of the bursa sac called bursitis. The result is a weakness in your upper arm that can be felt immediately.
Rotator cuff problems can fall along a wide spectrum of issues. The goal of surgical repair is to have the tendons heal back onto the bone, but this outcome isn’t always possible if the injury has significantly worsened over time. Having rotator cuff surgery, be it an open surgery or an arthroscopic surgery, will have a high chance of affecting your settlement value.
In other patients, a rotator cuff tear can result from an injury such as a fall. The goal of rotator cuff repair surgery is to help restore the function and flexibility of the shoulder and to relieve the. A complete tear is repaired by stitching the tendon back to its original site on the humerus.
“rotator cuff injury.” uw medicine orthopaedics and sports medicine: Often, the bursa is removed first, followed by removal of bone from the anteroinferior surface of acromion and release of. A rotator cuff is a group of muscles and tendons that support the shoulder joint and help you lift and move your arm.
Once fracture has been excluded, us or mri can be used to further assess the condition Surgery may be used where physiotherapy fails. A rotator cuff tear is a common shoulder injury that affects approximately two million people a year in the u.s., according to the american academy of orthopaedic surgeons (aaos).
Patients with degenerative rotator cuff tears may be managed conservatively, particularly where they are at increased risk of complications from surgery. Surgery for rotator cuff tears. Rotator cuff surgery is considered for healthy and motivated individuals in whom rotator cuff tears interferes with shoulder function.
Just because there is a tear, does not necessarily mean a surgery is needed. Rotator cuff tears are classified as either acute (lasting 3 months) tears; Successful rotator cuff surgery depends on a partnership between the patient and the experienced shoulder surgeon.
A weakness of the shoulder can occur and often clicking and crunching on movement. Often patients with rotator cuff tears come into the office complaining more of weakness, while patients with rotator cuff tendonitis (bursitis) complain predominantly of pain. Surgery for rotator cuff tears is increasingly performed mini‐invasively, either through a small incision or arthroscopically.
In patients over 60 years of age who undergo surgical rotator cuff repair, 33% will fail to heal after one year. Rotator cuff repair surgery typically is done as an outpatient procedure through a minimally invasive, or arthroscopic, approach. A partial tear, however, may need only a trimming or smoothing procedure called a debridement.
A partial tear, however, may need only a trimming or smoothing procedure called a debridement. Many sudden tears of the rotator cuff will cause direct, noticeably intense pain. This leads to pain, which can be severe.
Additional surgery is often required. After undergoing rotator cuff repair, the arm is kept in a sling for approximately six weeks after surgery to allow things to heal. The most common is inflammation of the rotator cuff called rotator cuff tendinitis.
Conservative versus surgical management for patients with rotator cuff tears: Traditionally, repairing rotator cuff tears involves complex shoulder surgery, either to stitch together or patch the torn area, or to reattach the tendon to the head of the humerus (upper arm bone). “arthroscopic shoulder surgery for the treatment of rotator cuff tears.”
Surgical techniques that may be used to repair a tear of the rotator cuff include arthroscopy, open surgery, or a combination of both. Patients will present with pain over the lateral aspect of shoulder and an inability to abduct the arm above 90 degrees; A complete tear within the thickest part of the tendon is repaired by stitching the two sides back together.
The patient�s motivation and dedication are important elements of the partnership.